Let’s talk about magnesium.
What Is Magnesium?
Magnesium is a mineral used in our bodies that is absorbed along our intestinal tract. Our levels of magnesium are closely regulated by our kidneys. Most of the magnesium in our body is stored in bone, muscle, and soft tissues (3). Magnesium serum concentrations (which would be the concentrations that you see when you have your blood drawn) would normally be in the range between 0.7 and 1.1 mM (3).
The Critical Pathways
Magnesium is essential as a cofactor in over 300 enzymatic reactions critical for metabolic pathways. Insufficient intake is widespread in Western populations, contributing to various health issues. (6)
The Role of Magnesium
Low levels of magnesium (AKA hypomagnesemia) may be a contributing factor in many functions of the body, including muscle cramps, high blood pressure, tightening of the arteries of the heart and/or brain, poor quality sleep, and low levels are linked to worsening insulin resistance. (5)
Some of the common diseases that contribute to hypomagnesemia would be different heart diseases, neuromuscular disfunction, malabsorption syndromes (when your body cannot absorb nutrients adequately), diabetes mellitus, kidney wasting syndromes, and alcoholism (2). Other causes of low magnesium may be the result of medication side effects and kidney dysfunction.
Vomiting and diarrhea, alcoholism, medication side effects, and inadequate intake of dietary magnesium are all general causes of low magnesium levels. “Estimations state that up to 60% of Americans do not meet daily magnesium requirements (3).”
How Do You Find Out if Your Blood Magnesium Levels Are Within a Normal Limit?
Although you can get your blood tested, unfortunately it isn’t very telling of your total magnesium stores since only 1% of your body’s total magnesium is found in the blood. A less invasive and more accurate way is to track your dietary intake and review it with a dietitian. You will notice that you may start having improved sleep, less muscle cramping, and improved blood pressure when you are more intentional about your magnesium intake.
Daily Magnesium Recommendations
The Food and Nutrition Board recommends: (4)
- 400-420 mg daily for men ages 31-50
- 310-320 mg daily for non-pregnant or lactating women ages 31-50
Where Is Magnesium Found?
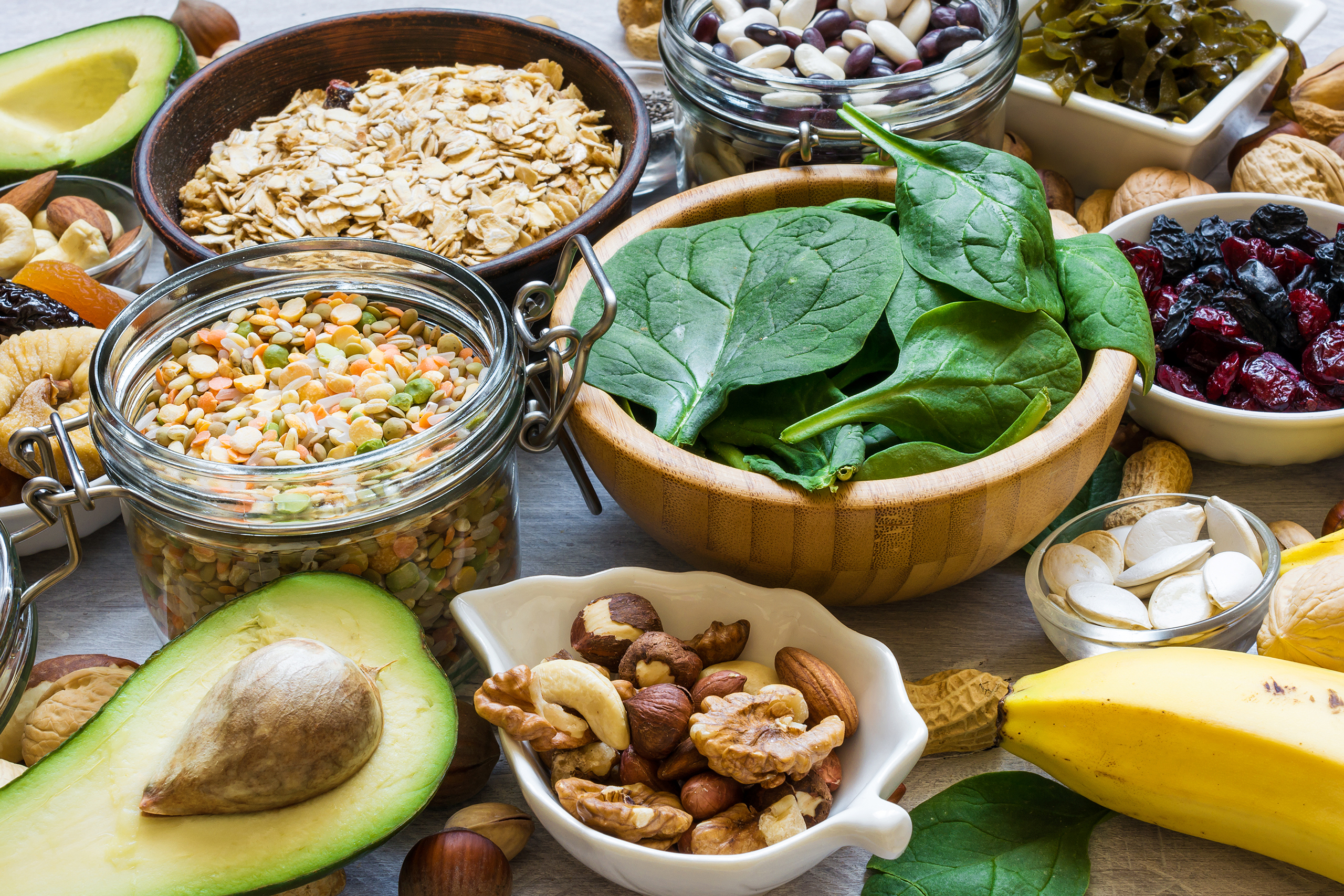
There are many sources of magnesium. It can be found naturally in many foods or be found in nutritional supplements.
Some of the natural sources of magnesium you may want to incorporate into your diet are:
- Pumpkin Seeds
- Chia Seeds
- Almonds
- Avocados
- Nuts
- Broccoli
- Legumes
- Peanut Butter
You should be getting most of your nutrients from food and beverages. Magnesium supplements can interact with medications and other supplements. For instance, they may impact the absorption of antibiotics if taken too soon before or after a supplement with magnesium (4). Before starting or stopping any supplements, you should consult with your health care professional.
By prioritizing adequate magnesium intake through mindful dietary choices and informed supplementation, you can support your body’s vital functions and enhance your overall health.
Sending Health Your Way!
The Tula Clinical Team
Reviewed by:
Aubree RN, BSN
Austin MS, RDN, CSR, LDN, CD
Tula Takeaways |
|---|
| 1. Essential Mineral: Magnesium is crucial for over 300 enzymatic reactions in the body, impacting metabolic pathways vital for overall health and well-being. |
| 2. Impact on Health: Low magnesium levels can contribute to various health issues such as muscle cramps, hypertension, cardiovascular problems, poor sleep quality, and worsened insulin resistance. |
| 3. Meeting Daily Needs: Despite its importance, a significant portion of the population, up to 60% in some estimates, does not meet daily magnesium requirements through diet alone. Ensuring adequate intake through dietary sources like nuts, seeds, and leafy greens is crucial, while supplements should be approached cautiously and under medical guidance to avoid interactions with medications. |
The LIVE TULA blog is informational and not medical advice. Always consult your doctor for health concerns. LIVE TULA doesn’t endorse specific tests, products, or procedures. Use the information at your own risk and check the last update date. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice.